BLOG
Introduction to Basic Knowledge of Wind Turbine
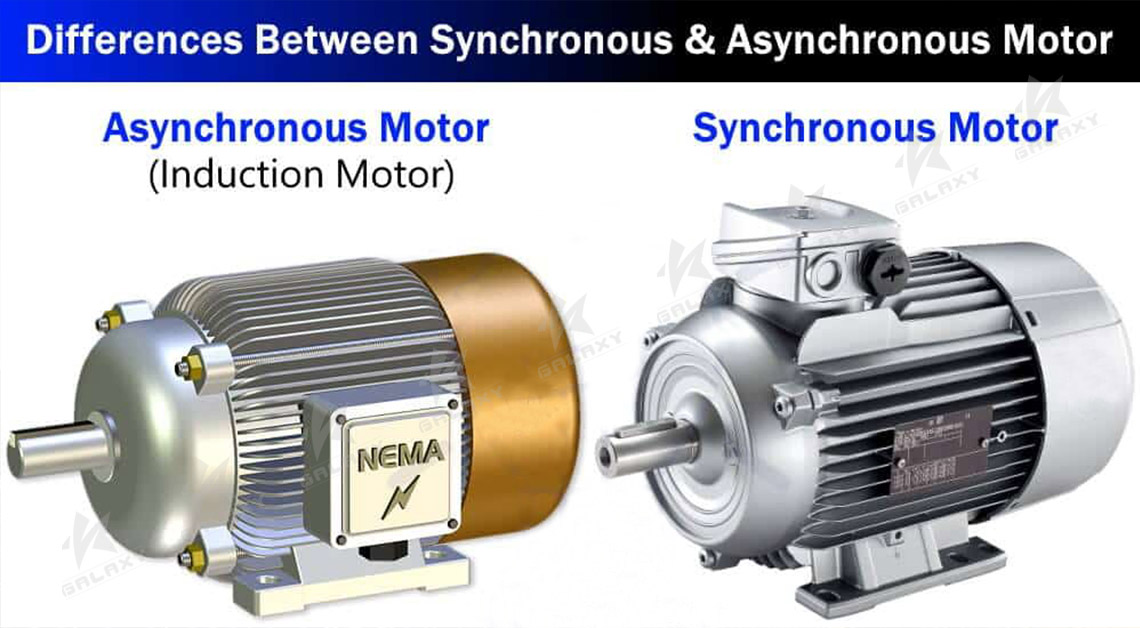
There are two main types of generators. Synchronous generators, also known as alternators, operate at exactly the same frequency as the grid to which they are connected. Asynchronous generators, which operate at a slightly higher frequency than the grid, are often called induction generators.
Both the induction generator and the synchronous generator have a non-rotating part called the stator. The two types of motors have similar stators. The stators of both types of motors are connected to the power grid and are composed of three-phase windings on the laminated iron core, which generate a magnetic field rotating at a constant speed when energized. Although the two motors have similar stators, their rotors are completely different. The rotor in a synchronous motor has a through-DC current winding, called the excitation winding, which establishes a constant magnetic field locking the stator winding to establish the rotating magnetic field. Therefore, the rotor can always rotate at a constant speed synchronized with the stator's magnetic field and the grid frequency. In some designs, the rotor field is generated by a permanent magnet machine, but this is not commonly used for large generators.
The rotor of an induction motor is different, for example, by a squirrel cage winding that is shorted at both ends. There is no electric connection between the rotor and the outside world. The rotor current is generated by the relative motion of the rotating magnetic field of the rotor cutting stator. If the rotor speed is exactly equal to the stator speed of the magnetic field (as in a synchronous generator), then there is no relative motion and no rotor induced current. Therefore, the total speed of the induction generator is always slightly higher than the stator rotating magnetic field velocity. The velocity difference is called slip, which is about 1% during normal operation.
Synchronous And Asynchronous Generators
Generators that convert mechanical energy into electrical energy are commonly used in synchronous excitation generators, permanent magnet generators and asynchronous generators. Synchronous generators are widely used in nuclear power, hydropower, thermal power and other conventional power grids. In wind power generation, synchronous generators can either supply power independently or be connected to the grid. However, when the synchronous generator is connected to the grid, it is necessary to have a synchronous detection device to compare the frequency, voltage and phase of the generator side and the system side, and adjust the wind generator so that the frequency of the generator is consistent with the system. Operate an automatic voltage regulator to adjust the generator voltage to the system voltage. At the same time, the speed of the wind turbine is fine-tuned to monitor from the periodic detection panel, so that the voltage of the generator is consistent with the voltage phase of the system. At the moment when the frequency, voltage and phase are synchronized, the circuit breaker is closed and the wind turbine is integrated into the system. The synchronous device can adopt manual synchronous grid connection and automatic synchronous grid connection. But generally speaking, synchronous generator is rarely used in grid-connected wind turbines because of its high cost and grid-connected trouble.
Control And Monitoring System
The operation and protection of wind turbines require a fully automatic control system, which must be able to control automatic starting, mechanical adjustment of blade pitch (in variable pitch wind turbines) and shutdown under normal and abnormal conditions. In addition to the control function, the system can also be used for monitoring to provide information on operating status, wind speed, direction, etc. The system is computer-based, and in addition to small wind turbines, control and monitoring can be carried out remotely. The control system has the following main functions:
1. Monitor the start, stop, alarm and operation signals in sequence control.
2. Low speed closed-loop control of yaw system.
3. Fast closed-loop control of pitch device (if it is variable pitch wind turbine).
4. Communication with wind farm controller or remote computer.
Fan Drive System
The mechanical energy produced by the blades of the impeller is transferred to the generator by the engine room's transmission system, which includes a gearbox, clutch and a braking system that can reset the wind turbine in the event of an emergency if it stops running. The gearbox is used to increase the impeller speed from 20 to 50 RPM to 1000 to 1500 RPM, which is the speed needed to drive most generators.
The gearbox can be a simple parallel shaft gearbox where the output shaft is not coaxial, or it can be a more expensive one that allows the input and output shafts to be collinear, making the structure more compact. The transmission system should be designed according to the output power and large dynamic torque load. Due to the fluctuating power output of the impeller, some designers try to control the dynamic load by increasing the mechanical adaptability and buffering drive. This is very important for large wind turbines because the dynamic load is large and the buffering margin of induction generators is less than that of small wind turbines.
Asynchronous Generator
Permanent magnet generator is a kind of generator that changes the rotor of ordinary synchronous generator into permanent magnet structure. Common permanent magnet materials include ferrite (BaFeO), samarium cobalt 5(SmCo), etc. Permanent magnet generator is generally used in small wind turbines.
Asynchronous generator refers to the asynchronous motor in the working state of power generation, from its excitation mode has the grid power supply excitation generation (separate excitation) and parallel capacitor self-excited generation (self-excitation) two cases.
1. Power grid excitation generation: The induction motor is connected to the power grid, the stator windings in the motor generate a rotating magnetic field rotating at synchronous speed, and then the prime mover is used to drag, so that the rotor speed is greater than the synchronous speed. The direction of the magnetic torque provided by the power grid must be opposite to the direction of the speed, and the direction of the mechanical torque is the same as the direction of the speed, then the mechanical energy of the prime mover is converted into electric energy. In this case, the active power emitted by the induction motor is transmitted to the power grid; At the same time, it also consumes the reactive power of the grid as excitation, and supplies the reactive power consumed by the stator and rotor magnetic leakage. Therefore, when the asynchronous generator is connected to the grid, it is generally required to add reactive power compensation device, usually by parallel capacitor compensation.
2. Self-excited power generation of shunt capacitors: The connection mode of shunt capacitors is divided into two kinds: star and triangle. In the process of generating electricity with its own residual magnetism, the generator periodically charges the capacitor. At the same time, the capacitor is also discharged periodically through the stator windings of the induction motor. This capacitor and winding composition of alternating charge and discharge process, constantly play the role of excitation, so as to make the generator normal generation. Excitation capacitors are divided into main excitation capacitors and auxiliary excitation capacitors. The main excitation capacitors are required to ensure the voltage establishment under no-load condition, while the auxiliary capacitors are designed to ensure the voltage constancy after accessing the load and prevent voltage collapse.
Through the above analysis, asynchronous generator starting, grid is very convenient and easy to automatic control, low price, reliable operation, convenient maintenance, operation efficiency is also high, so in wind power grid units are basically using asynchronous generators, and synchronous generators are often used for independent operation.